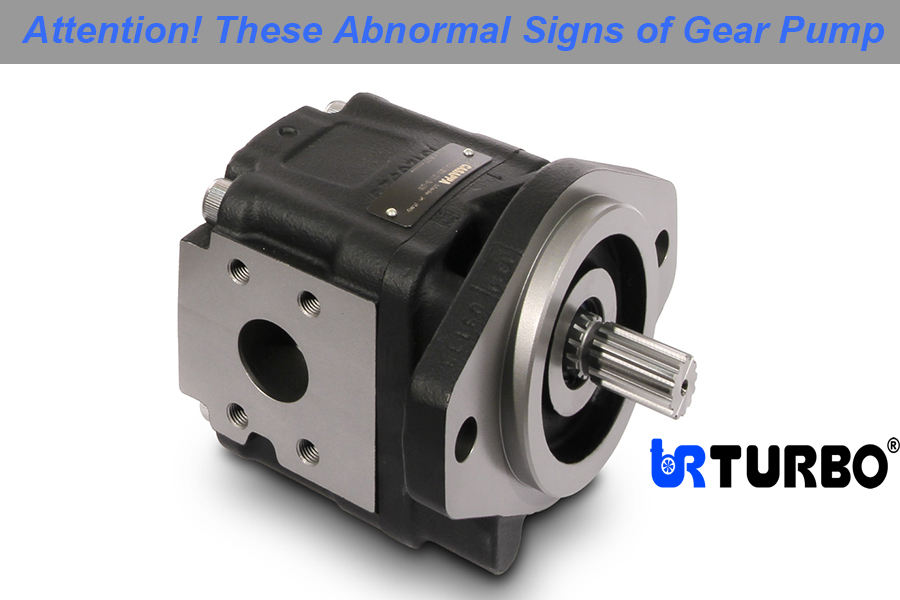
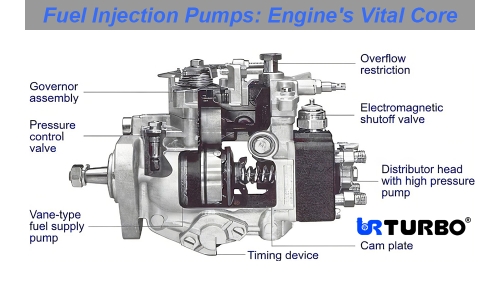
Attention! These Abnormal Signs of Gear Pump
Gear pumps, as a common hydraulic component, are widely used in excavators, loaders and other mechanical equipment. As an indispensable part of the hydraulic system, in the process of long-term operation, it is inevitable that some abnormal behavior will occur. If not dealt with in time, these abnormalities may lead to equipment failure, and even cause more serious safety accidents. Therefore, understanding the common abnormalities of gear pumps and their causes is essential for the maintenance and repair of equipment.
1. Abnormal noise
Gear pumps usually emit an even buzzing sound during normal operation. However, if the pump body emits abnormal noises, such as sharp metal friction sounds, irregular knocking sounds or obvious vibration sounds, this may be a sign that the gear pump is in trouble.
Possible causes:
Gear abrasion: after long-term use of the gears, the teeth are badly worn, resulting in poor meshing and noise.
Damaged bearings: bearings are the key components that support the gear operation, if the bearings are damaged, it will lead to unstable gear operation and generate noise.
Oil pollution: impurities or particles mixed in the oil may lead to increased wear of gears or bearings, which in turn generates noise.
Improper installation: Gear pumps are not aligned or fixed securely during installation, which may also lead to abnormal noise during operation.
Solution:
Check gears and bearings for wear and replace damaged parts in a timely manner. Keep the oil clean and replace or filter the oil regularly. Make sure the gear pump is installed correctly to avoid noise problems caused by improper installation.
2. Insufficient flow or pressure drop
The primary function of a gear pump is to provide a steady flow and pressure. If you find that the output flow rate of the pump is significantly reduced or the pressure drops, this may be an indication of a decline in the performance of the gear pump.
Possible causes:
Internal leakage: worn or damaged seals inside the gear pump cause oil to leak from the high pressure area to the low pressure area, resulting in a drop in flow and pressure.
Poor oil absorption: clogged suction line or clogged suction filter, resulting in the pump not being able to draw in enough oil, which in turn affects the flow rate and pressure.
Inappropriate oil viscosity: too high or too low oil viscosity will affect the working efficiency of the gear pump, resulting in abnormal flow and pressure.
Solution:
Check and replace worn seals and gears to ensure good internal sealing of the pump. Regularly clean the suction line and filter to ensure that the oil flows freely. Select the appropriate oil viscosity according to the equipment requirements.


3. Excessive temperature
Gear pumps generate a certain amount of heat during operation, but if the temperature of the pump body is too high, or even hot, this may be a sign of overloading or excessive internal friction in the gear pump.
Possible causes:
Overloaded operation: the gear pump has been running under overload for a long time, resulting in a higher temperature of the pump body.
Insufficient oil or poor oil quality: Insufficient oil or poor oil quality will lead to poor lubrication, increasing the friction of gears and bearings, which in turn leads to higher temperatures.
Excessive internal friction: Serious wear of gears or bearings leads to increased internal friction and generates a lot of heat.
Cooling system failure: If the gear pump is equipped with a cooling system, cooling system failure may also lead to high pump body temperature.
Solution:
Avoid prolonged overloading of the gear pump and make sure it is working under rated operating conditions. Check the oil quality and level regularly to ensure good lubrication. Check and repair the cooling system to ensure it is working properly.
4. Leakage
Leakage of gear pumps is usually manifested in the form of oil seeping out of the pump body or connections. Leakage not only causes waste of oil, but can also contaminate the environment and even pose a safety hazard.
Possible causes:
Aging or damage to seals: Gear pump seals (such as O-rings, oil seals, etc.) are aging or damaged, resulting in oil leakage.
Cracked or damaged pump body: The pump body is cracked due to external impact or long-term use, resulting in oil leakage.
Loose connection: the pump body and pipeline connection is loose or poor sealing, resulting in oil leakage.
Solution:
Regularly check the condition of seals and replace aged or damaged seals in time. Check the pump body for cracks or damage and repair or replace if necessary. Ensure that the connections between the pump body and piping are tight and avoid loosening.
The abnormal signs of the gear pump is often a precursor to equipment failure. Through timely detection and treatment of these abnormalities, you can effectively avoid equipment failure and extend the service life of the gear pump.